Transforming Education: Innovative Strategies for Engaging Students in the Classroom
Updated: 04 Jul 2025
Transforming Education
Changing schooling includes establishing a climate that cultivates commitment, decisive reasoning, and interest. Imaginative systems for drawing in understudies can assist them with taking responsibility for getting the hang of, prompting more significant and enduring instructive encounters. Here are a methodologies that teachers can use to connect with understudies really in the study hall:
1. Project-Based Learning (PBL)
- What It Is: Understudies work on a venture over a drawn out period, permitting them to jump profound into a subject of interest. The task comes full circle in a show or item that exhibits their learning.
- Why It Works: It makes learning more pertinent and active, assisting understudies with interfacing information with genuine applications. It likewise empowers joint effort, critical thinking, and autonomous reasoning.

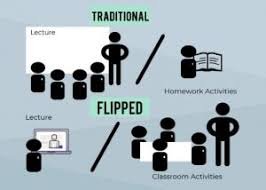
2. Flipped Classroom
- What It Is: Customary study hall learning is switched. Rather than learning new material in class, understudies advance at home (through recordings, readings, or different assets), and class time is utilized for drawing in exercises like conversations, undertakings, or critical thinking.
- Why It Works: It gives understudies more command over their learning pace and energizes dynamic picking up during class time. Educators can offer more customized help to understudies as they apply information.
3. Gamification
- What It Is: Applying game-like components to learning, like point frameworks, competitor lists, difficulties, or prizes, can make examples more tomfoolery and locking in.
- Why It Works: Gamification takes advantage of understudies’ cutthroat senses and rouses them to effectively partake. It causes figuring out how to feel more like a game and less like an undertaking, assisting understudies with staying drew in and determined.

4. Collaborative Learning
- What It Is: Understudies cooperate in little gatherings to tackle issues, lead research, or complete tasks.
- Why It Works: It creates social and relational abilities, energizes peer learning, and permits understudies to profit according to different points of view. Coordinated effort likewise sustains a feeling of local area in the study hall.

5. Personalized Learning
- What It Is: Fitting examples to meet the singular requirements, abilities, and interests of every understudy. This might include utilizing various sorts of learning devices or permitting understudies to pick subjects of interest for tasks.
- Why It Works: It permits understudies to learn at their own speed and such that suits their assets, which can expand inspiration and commitment.

6. Use of Innovation and Advanced Tools
- What It Is: Integrating tech apparatuses, for example, intelligent applications, computer experiences, online tests, and learning the executives frameworks to make illustrations more intuitive and dynamic.
- Why It Works: Innovation requests to computerized local understudies and opens up additional opportunities for imagination, cooperation, and admittance to immense data. It can make examples really captivating and versatile to various learning styles.

7. Real-World Connections
- What It Is: Interfacing the educational program to genuine issues and encounters, for example, having visitor speakers from different ventures, drawing in with local area projects, or investigating contemporary worldwide issues.
- Why It Works: Understudies see the pertinence of their advancing and how it applies outside the homeroom. This approach can encourage a more profound comprehension and inborn inspiration.

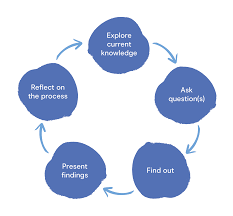
8. Inquiry-Based Learning
- What It Is: Understudies are urged to get clarification on some pressing issues, investigate subjects of revenue, and participate in exploration to find replies, as opposed to just getting data.
- Why It Works: It creates decisive reasoning and interest, permitting understudies to be the drivers of their learning. They connect profoundly with content since they are put resources into responding to their own inquiries.
9. Mindfulness and Social-Close to home Learning (SEL)
- What It Is: Incorporating care strategies and SEL rehearses into the homeroom assists understudies with dealing with their feelings, assemble strength, and foster sympathy.
- Why It Works: When understudies are genuinely and intellectually ready to learn, they are more engaged, drew in, and open to groundbreaking thoughts. SEL cultivates a positive and strong homeroom climate, improving understudy inspiration.

10. Flexible Learning Spaces
- What It Is: Making study halls with adaptable guest plans, admittance to different assets, and spaces intended for joint effort, innovativeness, and autonomous work.
- Why It Works: It permits understudies to work in conditions that suit their learning style, whether they need a peaceful space for center or a gathering region for joint effort.

11. Student Decision and Voice
- What It Is: Permitting understudies to have something to do with what, how, and when they learn. This could incorporate giving them choices for tasks, activities, or even homeroom schedules.
- Why It Works: It causes understudies to feel more put resources into their getting the hang of, realizing they have the opportunity to decide. It energizes self-course and obligation.

12. Active Learning Strategies
- What It Is: Utilizing procedures, for example, think-pair-share, pretending, contextual analyses, and intuitive conversations to connect with understudies effectively during class.
- Why It Works: Dynamic gaining shifts the concentration from latent paying attention to interest, which further develops maintenance and perception. It makes learning more intelligent and charming.

By integrating these imaginative techniques into the homeroom, teachers can establish a dynamic and steady learning climate that motivates understudies to connect all the more completely with the material, think fundamentally, and foster an enthusiasm for deep rooted learning.
Please Write Your Comments