Assistive Technology in Classrooms
Updated: 04 Jul 2025
Assistive technology includes devices and software that help students overcome learning barriers, such as screen readers or speech recognition tools.
It promotes accessibility and independence, allowing all students to participate fully.
By integrating these tools, classrooms become more inclusive and supportive of diverse needs.
Technology in classrooms
Assistive innovation (AT) in homerooms alludes to any apparatus, gadget, or framework that assists understudies with handicaps or learning difficulties to get to the educational plan and take part completely in the growing experience. It is a significant asset to guarantee that each understudy, no matter what their capacities, has an equivalent chance to prevail in their schooling.
Here are a few normal instances of assistive innovation utilized in homerooms:
1. Screen Readers
- Description: Programming that peruses text on a screen resoundingly, helpful for understudies with visual debilitations or dyslexia.
- Examples: JAWS, NVDA, or VoiceOver (for Macintosh).
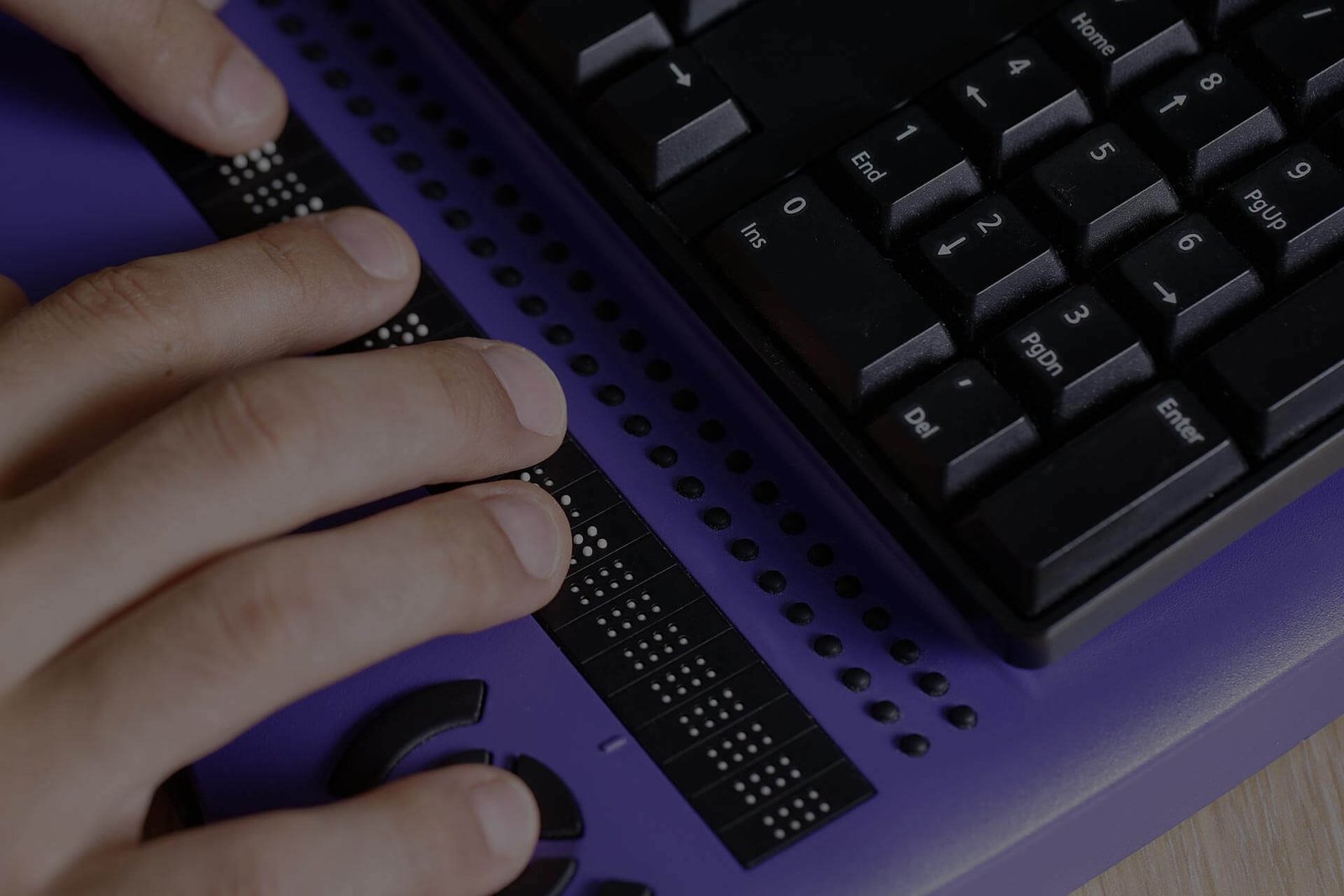

2. Speech-to-Text Software
- Description: This innovation changes over verbally expressed words into composed text, which can be useful for understudies with learning handicaps, like dysgraphia, or actual incapacities that make composing troublesome.
- Examples: Winged serpent NaturallySpeaking, Google Voice Composing.

3. Audio Books and Bookshare
- Description: These permit understudies to pay attention to course books, books, or other instructive materials, which assists understudies with understanding inabilities or vision impedances.
- Examples: Discernible, Bookshare, Learning Partner.

4. Text-to-Discourse Tools
- Description: These devices can recite without holding back any text that is shown on a screen. They help understudies who battle with perusing or figuring out composed text.
- Examples: Kurzweil 3000, Read&Write.

5. Word Processors with Word Prediction
- Description: These assistance understudies with hardships in spelling, composing, or coordinating their considerations by recommending words or finishing sentences.
- Examples: Co:Writer, Ghotit Genuine Essayist.

6. Alternative Consoles or Mouse Devices
- Description: Uncommonly planned consoles or mice for understudies with actual handicaps, making it more straightforward for them to associate with PCs and other computerized apparatuses.
- Examples: Intellikeys, adjusted mice, touchscreens.

7. Video Captioning
- Description: Permits video content to be joined by inscriptions or captions, helping understudies who are hard of hearing or deaf.
- Examples: YouTube’s programmed subtitles, inscribed instructive recordings.

8. Organizational Tools
- Description: Devices to assist understudies with leader working issues, like using time productively, association, or arranging.
- Examples: Visual timetables, clocks, applications like Google Schedule or Trello.

9. Hearing Helps and FM Systems
- Description: Gadgets that intensify sound for understudies with hearing weaknesses, assisting them with bettering hear guidelines and homeroom exercises.
- Examples: Individual portable hearing assistants, FM enhancement frameworks.

10. Communication Gadgets for Non-Verbal Students
- Description: These apparatuses help understudies who are non-verbal or have discourse challenges in speaking with others.
- Examples: Augmentative and Elective Correspondence (AAC) gadgets like the Tobii Dynavox or PECS (Picture Trade Correspondence Framework).

11. Math Programming and Tools
- Description: These devices assist understudies who with battling with math ideas and computations by offering elective ways of moving toward issues.
- Examples: ModMath, Ghotit Genuine Author for math, talking number crunchers.

Advantages of Assistive Innovation in Homerooms:
- Expanded independence: Understudies can perform undertakings on their own that could somehow or another be troublesome.
- Engagement: Intelligent and customized learning devices can expand inspiration and consideration.
- Comprehensive education: Permits understudies with incapacities to get to the overall training educational program close by their companions.
- Customization: Innovation can be custom-made to address individual issues, whether it’s a particular learning incapacity or actual restriction.
Challenges:
- Cost: Numerous assistive innovation devices can be costly.
- Training: Educators and understudies might require preparing to utilize these instruments really.
- Compatibility: Some innovation may not be viable with existing study hall frameworks or gadgets.
Consolidating assistive innovation in homerooms helps overcome any issues for understudies who could somehow confront boundaries in customary learning conditions. With progressing headways, there are more open doors than any other time for schools to carry out innovation that cultivates comprehensive, viable learning.